What is Radon?
- Radon is a colorless, odorless naturally occurring radioactive gas that is produced by the breakdown of uranium in the earth's crust.
- Radon is the number one cause of lung cancer in non smokers, second only to the number of lung cancer incidents from cigarette smoking. If you are a smoker, you are at much greater risk of getting lung cancer when combined with elevated radon levels in your home or office.
- Radon is a Class A carcinogen.
- As you breath, radon gas enters and exits your lungs.
- Decay products can become lodged in your lungs.
- Alpha radiation is released as the Radon Gas decays
- Alpha Radiation can cause damage the DNA of lung tissue
- Radon is estimated to cause approximately 21,000 lung cancer deaths per year.
From the Atom on:
It takes about 4.5 billion years for uranium to decay into radium and then another 1,620 years to change from a solid state to radon gas. Radon gas then changes form and begins to decay and spontaneously release radiation, with a half-life of approximately 3.8 days. Half-life is the time required for one half the atoms of a given amount of a radioactive substance to disintegrate
SHOW FLOWCHART OF DECAY CHAIN WITH ALPHA AND BETA RELEASE
Radon 222 - Polonium218 - Lead 214 - Bismuth 214 - Lead 210
Polonium 218 and 214 from the radon gas decay chain release Alpha radiation. Alpha radiation does the most damage to the lung cell tissue. Alpha radiation moves slower and with greater impact than gamma and beta radiation, which are also released during the radon decay process. The energy emission travels less than a few inches, but is strong enough to pit plastic in the long term alpha track testing devices.
SHOW SLIDE OF ALPHA TRACK TEST DEVICE WITH PITTED PLASTIC
To understand the characteristics of radon and it's decay products, think in terms of a continuous process of subatomic particles changing from mass into energy and from energy into mass. Radon gas prior to decay is a noble inert gas, meaning it doesn't interact, or bond with other atoms (or lung tissue). It is the decay chain particles, and the alpha radiation release that causes lung cancer.
Alpha, Beta and Gamma radiation emissions are given off throughout the decay series
While colorless, odorless and tasteless, Alpha energy release from the radon atom can be seen for scientific observation within what is known as a cloud chamber. Below is a picture of the release of the alpha radiation from a radon atom within a cloud chamber.

Radon is measured in PiccoCurries per Liter of Air, (pCi/L). Pico = one trillionth. And 1pCi/L = 2.22 decays per minute per liter of air. So then, 4pCi/L equals 10 decays per liter of air per minute. It would take approximately 2,500 radon atoms per square inch to create a radon concentration of 4pCi/L.
Radiation
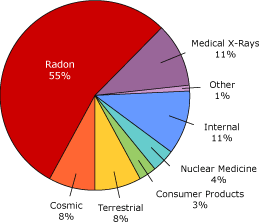
Radon is considered a low level amount of radiation and everyone is exposed to natural radiation everyday. Radon gas accounts for 55% of a typical person's radiation exposure followed by CAT scans as the second leading source of radiation exposure at 11%.
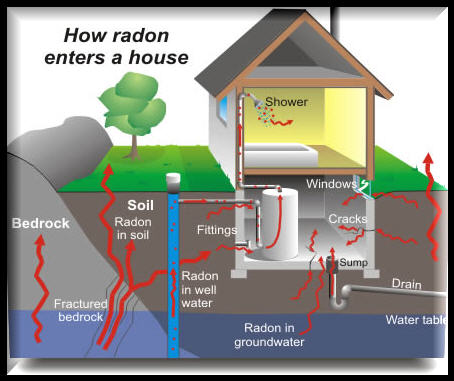
How Radon Enters a Home
Radon gas enters the home through the slab, basement, or crawl space. Pressure differences within the home (from warm air rising and other natural effects) pull radon into living spaces from the soil. Furnace & air conditioning systems can distribute the air through the structure.
Any home may have a radon problem, new or old with or without a basement, sealed basement or not.
Radon from soil gas is the main cause of radon problems. Other less common sources include well water and building materials. Measuring radon concentration in the air is recommended for initial testing.
Nearly 1 out of every 3 homes in Missouri is estimated to have elevated radon levels.