How Radon Enters Your Home
Radon gas enters the home through the slab, basement, or crawl space. Pressure differences within the home (from warm air rising and other natural effects) pull radon into living spaces from the soil. Furnace & air conditioning systems can distribute the air throughout the entire house.
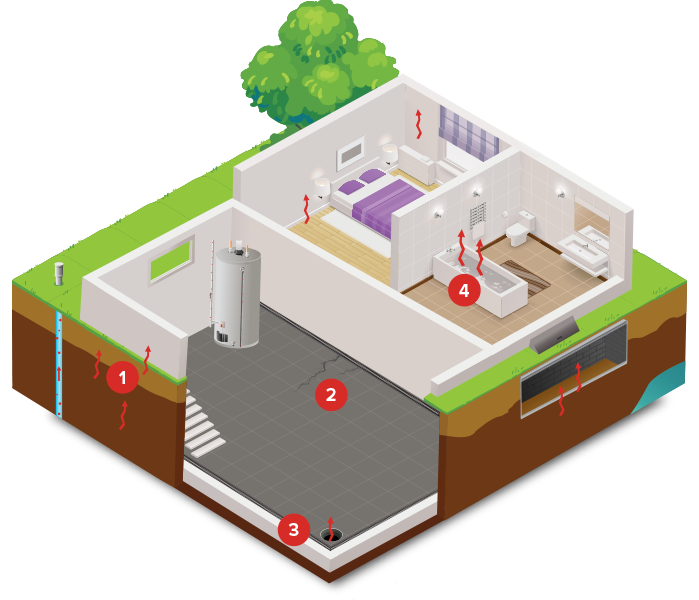
How Radon Enters Your Home

Soil
Uranium deposits int the soil and rock are the main cause of elevated radon levels in your homes. The pressure difference between the inside and outside of your home, your home creates a vacuum that pulls radon through foundation cracks and other openings.

Cracks
All exposed cracks and other openings in the floor of the lowest level of the home can allow Radon to enter your home. Because radon is a radioactive gas, it can enter the home without cracks or openings. While sealing cracks can be beneficial to the radon systems performance, sealing is not recommended as a stand alone solution.

Drainage
An open drain tile system (a gap between the concrete floor and wall) will allow radon to enter in the home at a faster rate and increase the levels of radon. A sump can also be another area where Radon can enter your home. Radon levels should be checked if either of these improvements have been made to your home since your last radon test.

Water
Radon entering the home through water is a small risk compared with radon entering your home from the soil. Well water can can bring Radon into the home through the shower or other water sources.
While sealing may be a necessary part of the radon mitigation process, the EPA does not recommend the use of sealing alone to reduce radon because by itself, sealing has not been shown to lower radon levels significantly or consistently.
Any home may have a radon problem, new or old with or without a basement, sealed basement or not.
Radon from soil gas is the main cause of radon problems. Other less common sources include well water and building materials. Measuring radon concentration in the air is recommended for initial testing.