From The Atom On
Radon gas prior to decay is a noble inert gas, meaning it doesn't interact, or bond with other atoms (or lung tissue). It is the decay chain particles, and the alpha radiation release that causes lung cancer.

Alpha Radiation emissions from the radon gas decay chain does the most damage to the sensitive lung cell tissue. Alpha radiation moves slower and with greater impact than gamma and beta radiation. The energy emissions travel less than a few inches, but are strong enough to pit plastic as shown below on the surface of the long term alpha track radon testing device.
To understand the characteristics of radon and it's decay products, think in terms of a continuous process of subatomic particles changing from mass into energy and from energy into mass.
It takes about 4.5 Billion years for uranium to decay into Radium and then about another 1,600 years to change from a solid state to radon gas. Radon gas then changes form and begins to decay and spontaneously release radiation, with a half life of approximately 3.8 days.
Radon has a half-life of about 3.8 days -- half of a given quantity of it breaks down every 3.8 days. When radon undergoes radioactive decay, it emits ionizing radiation in the form of alpha particles. It also produces short-lived decay products, often called progeny or daughters, some of which are also radioactive.
Unlike radon, the progeny are not gases and can easily attach to dust and other particles. Those particles can be transported by air and can also be breathed. The decay of progeny continues until stable, non-radioactive progeny are formed. At each step in the decay process, radiation is released.
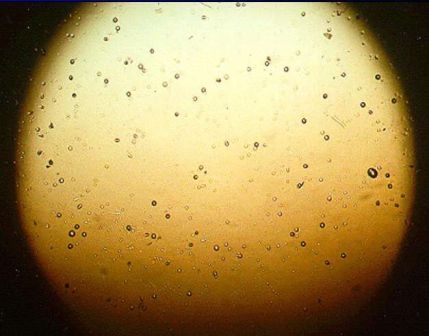
While colorless, odorless and tasteless, Alpha energy release from the radon atom can be seen for scientific observation within what is known as a cloud chamber. Below is a picture of the release of the alpha radiation from a radon atom within a cloud chamber.

Sometimes, the term radon is used in a broad sense, referring to radon and its radioactive progeny all at once. When testing measures radiation from the progeny, rather than radon itself, the measurements are usually expressed in working level (WL) units. When radiation from radon is measured directly, the amount is usually expressed in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L).